Introduction
Imagine stepping into a medieval castle, battling dragons, or exploring distant planets without leaving your living room. Or picture trying on clothes virtually before buying them online. These experiences are made possible by Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR), two groundbreaking technologies that blend digital and physical worlds. VR immerses users in entirely virtual environments, while AR overlays digital information onto the real world. This article delves into what VR and AR are, how they work, their real-world applications, current trends, and their potential to transform our lives, all presented in an engaging and accessible way.
What are Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality?
Virtual Reality (VR)
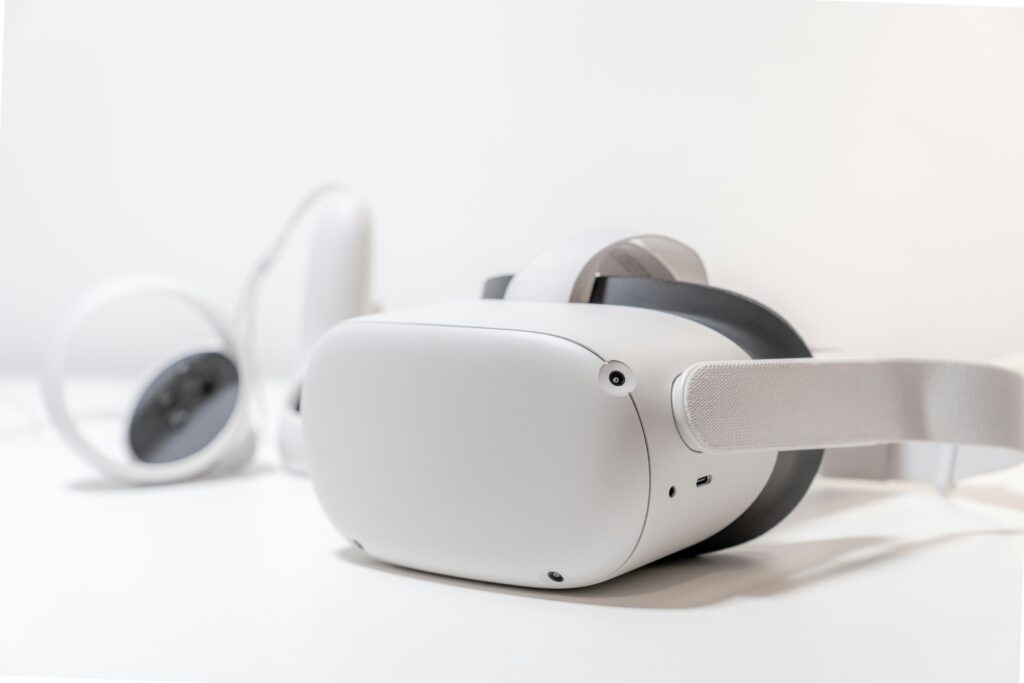
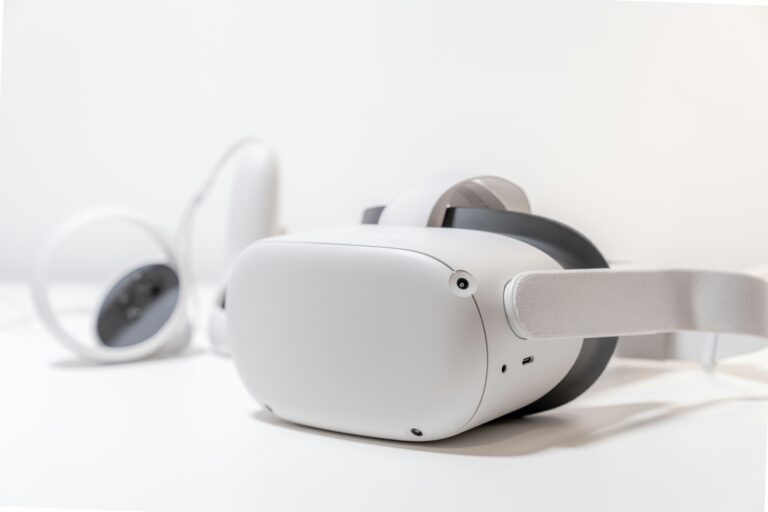
VR creates a fully immersive digital environment that replaces the real world. Users wear headsets, like the Meta Quest or PlayStation VR, equipped with screens, sensors, and motion trackers to experience 360-degree virtual spaces. VR tricks the senses, making you feel as if you’re “inside” the digital world, whether it’s a game, simulation, or virtual tour.
Augmented Reality (AR)
AR enhances the real world by overlaying digital elements, such as images, text, or animations, viewed through devices like smartphones, tablets, or AR glasses (e.g., Apple Vision Pro). Unlike VR, AR doesn’t replace reality but augments it. For example, Pokémon GO uses AR to place virtual creatures in real-world locations via your phone’s camera.
Key Differences
- Immersion: VR is fully immersive, isolating users from the real world; AR integrates digital content with reality.
- Devices: VR requires headsets; AR often works on everyday devices like phones or lightweight glasses.
- Use Cases: VR suits simulations and entertainment; AR excels in real-time information and interaction.
How VR and AR Work
Both technologies rely on advanced hardware and software to create seamless experiences.
VR Technology
- Headsets: Display high-resolution visuals and track head movements using gyroscopes and accelerometers.
- Controllers: Allow users to interact with the virtual environment, like swinging a sword in a game.
- Tracking Systems: External sensors or cameras map the user’s position in physical space to prevent collisions.
- Software: Renders 3D environments and processes inputs for real-time interaction.
For example, in a VR game like Beat Saber, the headset displays a rhythmic world, controllers track your hand movements to slice blocks, and software syncs visuals with music.
AR Technology
- Cameras and Sensors: Capture the real-world environment and track objects or surfaces.
- Displays: Project digital overlays on screens or transparent lenses.
- Processing Units: Use computer vision and AI to align virtual content with the physical world.
- Software: Powers apps to deliver context-aware information, like navigation directions or product details.
In IKEA’s AR app, your phone’s camera scans a room, and the app overlays virtual furniture, adjusting for scale and perspective.
Behind every good headline is research — and behind every good trade is strategy. Dive into the finance section now.
Real-World Applications of VR and AR
VR and AR are transforming industries by offering innovative solutions and immersive experiences.
Entertainment and Gaming
VR gaming, like Half-Life: Alyx, delivers unparalleled immersion, letting players explore sci-fi worlds. AR games, such as Pokémon GO, encourage real-world exploration. Beyond gaming, VR is used for virtual concerts, and AR enhances live events with interactive overlays.
Education and Training
VR simulations train professionals in risk-free environments. Medical students practice surgeries using VR platforms like Osso VR, while pilots hone skills in flight simulators. AR aids education by overlaying interactive diagrams, as seen in apps like Google Expeditions, which lets students explore historical sites.
Healthcare
VR helps treat mental health conditions, such as anxiety or PTSD, through exposure therapy in controlled virtual settings. AR assists surgeons by projecting 3D models of organs during operations, improving precision. For example, Microsoft’s HoloLens is used in surgical planning.
Retail and E-commerce
AR enhances shopping by letting customers visualize products. Sephora’s Virtual Artist app uses AR to show how makeup looks on your face, while IKEA’s app places furniture in your home. VR showrooms, like those by Audi, let customers explore car models virtually.
Architecture and Design
VR allows architects to walk clients through virtual buildings before construction begins, using tools like Autodesk Revit. AR helps designers overlay blueprints on physical sites, ensuring accuracy during construction.
Current Trends in VR and AR
As of June 2025, VR and AR are advancing rapidly, driven by technological breakthroughs and growing adoption.
Lightweight and Affordable Devices
VR headsets are becoming more compact and affordable, with devices like Meta Quest 3 offering high-quality experiences at lower prices. AR glasses, such as Snap’s Spectacles, are sleeker, resembling regular eyewear, encouraging mainstream use.
5G and Cloud Integration
5G networks reduce latency, enabling smoother VR/AR experiences, especially for cloud-based rendering. This allows high-end graphics on lightweight devices, as seen in cloud VR platforms like NVIDIA’s GeForce Now.
Mixed Reality (MR)
Mixed reality, blending VR and AR, is gaining traction. Devices like Apple Vision Pro combine immersive VR with AR overlays, supporting applications from gaming to professional collaboration.
AI-Powered Experiences
AI enhances VR/AR by creating dynamic environments and personalized content. For instance, AI-driven NPCs (non-player characters) in VR games react realistically, while AR apps use AI to recognize objects and provide context-aware information.
Social and Metaverse Applications
The metaverse—a shared virtual space—relies on VR/AR. Platforms like Horizon Worlds enable virtual socializing, work, and events. AR is used for real-world metaverse interactions, such as digital art installations in public spaces.
Challenges of VR and AR
Despite their promise, VR and AR face hurdles:
- Cost: High-end devices remain expensive, though prices are dropping.
- Health Concerns: Prolonged VR use can cause motion sickness or eye strain; AR must ensure user safety during real-world navigation.
- Privacy: AR devices collecting real-world data raise concerns about surveillance and data security.
- Content Development: Creating high-quality VR/AR content is resource-intensive, limiting variety.
- Accessibility: Ensuring these technologies are inclusive for users with disabilities is critical.
Addressing these challenges requires innovation, regulation, and user education.
The Future of VR and AR
The future of VR and AR is bright, with transformative potential across industries. By 2030, analysts predict widespread adoption, driven by:
- Education Revolution: VR/AR could personalize learning, making education immersive and accessible globally.
- Workplace Transformation: Remote collaboration in virtual offices will become common, reducing travel costs.
- Healthcare Advancements: VR/AR could enable remote surgeries and advanced therapy for mental health.
- Consumer Integration: AR contact lenses and brain-computer interfaces may make these technologies seamless parts of daily life.
Investment in infrastructure, skills, and ethical frameworks will be key to realizing this potential.
Conclusion
Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality are reshaping how we interact with the world, offering immersive and interactive experiences that were once the stuff of science fiction. From gaming and education to healthcare and retail, their applications are vast and growing. As trends like AI integration, 5G, and mixed reality drive innovation, VR and AR promise a future where digital and physical realities blend seamlessly. By overcoming challenges like cost and privacy, these technologies can unlock new possibilities, creating a more connected and engaging world for all.